| FIELD
SAMPLING AND ANALYSIS MATRIX: FIELD SAMPLING AND COLLECTION TECHNIQUES |
| Italics Most commonly used field techniques from
Subsurface Characterization and Monitoring Techniques EPA 625-R-93-003 See Legend below for explanation, or switch to the text-based version if this loads too slowly.
Technique / Instrumentation |
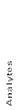
|
MEDIA |
|
 |
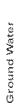 |
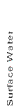 |
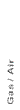 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 3 ACCESS TOOLS |
| 3.1
Drilling Methods - Unconsolidated Formations |
| 3.1.1 Hollow-Stem Auger |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.1.2 Direct
Mud Rotary |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.1.3 Directional
Drilling |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.1.4 Solid
Flight and Bucket Augers |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.1.5 Jetting
Methods |
2, 4-6, 10, 11 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.1.6 Sonic
Drilling |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.2
Drilling Methods - Consolidated Formations |
| 3.2.1 Direct
Air Rotary with Rotary Bit / Downhole Hammer |
2, 4-6, 10, 11 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.2.2 Cable Tool |
2, 4-6, 10, 11 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.2.3 Rotary
Diamond Drilling |
2, 4-6, 10, 11 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.3
Drive Methods |
| 3.3.1 Cone
Penetrometer |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.3.2 Direct
Push Sampler |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.4
Sampling Installations for Portable Samplers |
| 3.4.1 Driven
Wells |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.4.2 Single Riser / Limited Interval Wells |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 3.4.3 Nested
Wells / Single Borehole |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.4.4 Nested
Wells / Multiple Boreholes |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.5
Portable In-Situ Ground Water Samplers / Sensors |
| 3.5.1 Direct
Drive Samplers |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.5.2 Passive
Multilayer Samplers |
1, 3 |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.6
Fixed In-Situ Samplers |
| 3.6.1 Multilevel
Capsule Samplers |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.6.2 Multiple-Port
Casings |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.6.3 Passive
Multilayer Samplers |
1, 3 |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.7
Destructive Sampling Methods |
| 3.7.1 Coring
and Extraction |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 3.7.2 Temporary
Installations |
All |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4 COLLECTION TOOLS |
| 4.1
Hand-Held Methods |
| 4.1.1 Scoops,
Spoons, and Shovels |
All |
 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.1.2 Augers |
All |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.1.3 Tubes |
All |
 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.2
Power-Driven Soil Samplers |
| 4.2.1 Split
and Solid Barrel |
All |
 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.2.2 Rotating
Core |
2, 4-6, 10, 11 |
 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 4.2.3 Thin-Wall
Open Tube |
All |
 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.2.4 Thin-Wall
Piston / Specialized Thin Wall |
All |
 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.3
Portable Positive Displacement |
| 4.3.1 Bladder
Pump |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.3.2 Gear
Pump |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
I |
No |
 |
| 4.3.3 Submersible
Helical Rotor Pump |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
I |
No |
 |
| 4.3.4 Gas-Driven
Displacement Pumps |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.3.5 Gas-Driven
Piston Pumps |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 4.4
Other Portable Ground Water Sampling Pumps |
| 4.4.1 Suction-Lift
Pumps (peristaltic) |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.4.2 Submersible
Centrifugal Pump |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.4.3 Inertial-Lift
Pumps |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 4.5
Portable Grab Samplers |
| 4.5.1 Bailer |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.5.2
Pneumatic Depth-Specific Samplers |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 4.5.3 Mechanical
depth-Specific Samplers |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.6
Extractive Collection Methods |
| 4.6.1
Soil Water Extraction |
All |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 4.6.2 Sorbent
Devices |
All |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.6.3 Biological
Indicators |
All |
 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 4.7
Gas / Air Collection Methods |
| 4.7.1 Soil
Gas Sampling (static) |
1, 3 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.7.2 Soil
Gas Probes |
1, 3 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 4.7.3 Air
Sampling Devices |
1, 3 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
III |
No |
NA |
| 5 EXTRACTION METHODS |
| 5.1 Solvent
Extraction |
1-7, 10, 11 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 5.2 Thermal
Digestion |
7-9 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 5.3 Thermal
Extraction / Desorption |
2, 4, 5 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
| 5.4 Purge
and Trap |
1, 3 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 5.5 Headspace |
1, 3 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
III |
No |
 |
| 5.6 Supercritical
Fluid Extraction |
2, 4, 5, 10 |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
NA |
 |
 |
I |
No |
 |
| 5.7 Membrane
Extraction |
1, 3 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
I |
No |
 |
| 5.8 Sorbent
Extraction |
1-10 |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
NA |
 |
 |
II |
No |
 |
